Understanding Typhoid Fever: Symptoms, Transmission, and Serological Testing Strategies
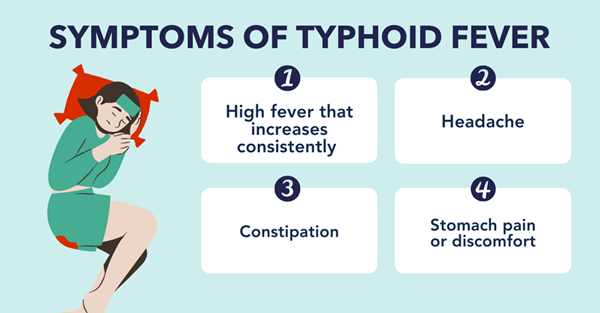
Typhoid fever is an acute intestinal infectious disease caused by Salmonella Typhi. It is primarily transmitted through contaminated food or water and is particularly common in areas with poor sanitation. Typical symptoms include persistent high fever, abdominal pain, a roseola rash, a relatively bradycardia, and hepatosplenomegaly. Severe cases can cause intestinal perforation or bleeding, and can even be life-threatening. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to controlling the progression of the disease and reducing mortality, and serological testing plays a key role in this process.
Transmission routes and high-incidence areas
Typhoid fever is primarily transmitted through the fecal-oral route. Stool from infected individuals or carriers carries large numbers of bacteria, which can contaminate water or food, potentially infecting others. The disease remains widespread in developing countries such as Africa, South Asia, and Southeast Asia, particularly in areas with weak sanitation infrastructure and inadequate access to clean drinking water. Travelers to high-risk areas are also susceptible to infection if they fail to take adequate precautions.
Serological testing protocols for typhoid fever
Early diagnosis of typhoid fever is challenging, as its symptoms often mimic those of other febrile illnesses, such as malaria and dengue fever. Blood culture is the gold standard for confirming typhoid fever, but this method is time-consuming (typically taking several days), and its sensitivity is affected by factors such as collection time and antibiotic use. Therefore, serological testing is widely used as a supplementary diagnostic tool due to its rapidity and simplicity.
- Widal Test
The Widal test is a traditional serological assay for typhoid fever, used to detect antibody titers against O (somatic antigen) and H (flagellar antigen) in the patient’s serum. Antibody levels typically begin to rise about one week after symptom onset.- Operational requirement: Paired serum samples from both the acute and convalescent phases are needed. A fourfold or greater increase in antibody titer is considered diagnostically significant.
- Limitations: The test has relatively low specificity and may yield false-positive results (e.g., due to prior vaccination or infection with other Salmonella serotypes). It also has limited sensitivity in the early stages of the disease.
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
In recent years, ELISA technology has been widely used to detect typhoid-specific antibodies (such as anti-Vi antigen IgG and IgM), offering high sensitivity and specificity.- Advantages: It can distinguish acute infection (IgM-positive) from previous infection or carrier status (IgG-positive). A single serum sample can provide a reference result, significantly shortening diagnostic time.
- Application: It is particularly suitable for areas with limited medical resources or as a rapid screening tool during epidemic outbreaks.
- Other Rapid Testing Methods
Rapid test kits such as colloidal gold immunochromatographic tests have also been put into use, which can provide preliminary results within 15–20 minutes and are suitable for primary care institutions and on-site screening.
Although serological testing has the advantages of being rapid and convenient, its results should be comprehensively judged in combination with the patient’s clinical manifestations, epidemiological history, and other laboratory tests (such as blood culture and PCR molecular testing) to avoid misdiagnosis.
Prevention and Treatment
The most effective ways to prevent typhoid fever are to maintain personal hygiene, drink safe water, and get vaccinated against typhoid fever. Once diagnosed, antibiotics should be used promptly for treatment. However, the increase in drug-resistant strains in recent years has brought new challenges to clinical treatment.
In summary, typhoid fever continues to threaten public health in many regions around the world. Serological testing, as an important auxiliary diagnostic tool, is expected to further improve the early diagnosis rate of typhoid fever with the support of continuously optimized technologies, providing support for effective control of disease transmission.
Baysen Medical is always focus on diagnostic technique to improve the quality of life . We have developed 5 technology platforms- Latex , colloidal gold , Fluorescence Immunochromatographic Assay , Molecular,Chemiluminescence Immunoassay.We have Typhoid IgG/Igm Rapid test for screening early-stage kidney injury.
Post time: Sep-08-2025